Struggling with cold storage management in your distribution business? Discover how optimizing your cold storage solutions can enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure product integrity. Explore effective strategies and innovative tools to streamline your operations and boost customer satisfaction.
Imagine the peak of summer: the sun blazes outside, and across the country, customers are flocking to retail stores in search of refreshments, frozen foods, and other perishable goods. Behind the scenes, distributors of all sizes—from those serving small convenience stores to large supermarket chains—are the unsung heroes ensuring that every product remains perfectly chilled, thanks to their state-of-the-art cold storage solutions. This scenario underscores the critical role efficient cold storage plays across the distribution industry, ensuring product integrity, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of cold storage, providing you with in-depth tips, best practices, and innovative strategies to optimize your operations. Whether you’re new to the distribution industry or looking to enhance your existing cold storage solutions, this comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary for success.
Assessing Your Needs: Cold Storage Warehouses vs. Coolers and Freezers
As we delve into the world of cold storage, it’s important to recognize that not all distribution operations require extensive cold storage warehousing. Many distributors, particularly those catering to convenience stores and small retail outlets, find that their needs are efficiently met with well-managed coolers and freezers. Understanding this distinction is crucial. You’ll need to balance operational efficiency with the practicalities of space, budget, and the requirements of the products you distribute.
To assess your needs, start by considering the volume of perishable goods, the range of products, and the speed at which they move through your supply chain. This can significantly impact whether you need a dedicated cold storage warehouse or if simpler cooling solutions will suffice.
With all of this in mind, let’s dive into why cold storage matters so much.
Understanding the Importance of Cold Storage Solutions
For distributors, cold storage is more than just a facility; it’s a crucial component of the supply chain. Proper cold storage ensures that perishable products like snacks, food and beverages, and pharmaceuticals are stored at the correct temperatures, maintaining quality and safety from warehouse to point of sale. But navigating the complexities of cold storage to find the best solutions for your business can be challenging.
The significance of cold storage extends beyond merely preserving perishable goods; it’s integral to maintaining a seamless supply chain, ensuring products reach consumers in optimal condition. This is particularly crucial in a world where consumer expectations for quality and freshness are higher than ever. A robust cold storage system not only helps in meeting these expectations but also plays a vital role in minimizing waste, a key concern for distributors aiming for sustainability and efficiency.
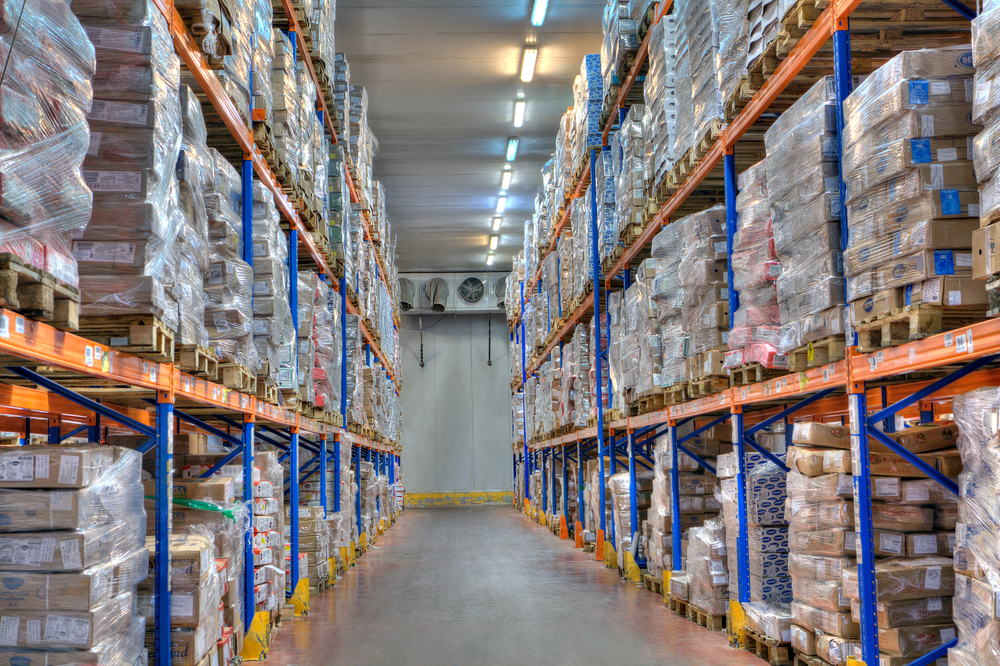

Key Benefits of Effective Cold Storage Solutions
- Product Integrity: By maintaining precise temperature control, cold storage solutions help in preserving the nutritional value, appearance, and taste of perishable products, ensuring they reach the consumer as intended.
- Compliance and Safety: Regulatory compliance is a major consideration for distributors. Effective cold storage solutions ensure that products are stored and transported within the temperature ranges mandated by food safety regulations, helping businesses avoid costly penalties and protect consumer health.
- Operational Efficiency: Advanced cold storage solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency through better inventory management, reduced energy consumption, and minimized product loss due to spoilage.
- Market Expansion: With reliable cold storage solutions, distributors can expand their market reach by safely transporting perishable goods over longer distances, opening up new markets and customer bases.
Types of Cold Storage Solutions
Choosing the right type of cold storage solution is crucial for maintaining the integrity of perishable goods throughout the supply chain. Distributors have several options, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Here’s an overview of the most common types of cold storage solutions:
Walk-in Coolers and Freezers
Ideal for both small-scale and large-scale operations, walk-in coolers and freezers offer customizable sizes and specifications to suit various storage needs. They are commonly used in restaurants, grocery stores, and distribution centers for storing products that require refrigeration or freezing.
- Advantages: Customizable sizes, flexible temperature settings, and relatively easy to install.
- Considerations: Energy consumption and the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Refrigerated Containers (Reefers)
Refrigerated containers, or reefers, are portable cold storage units that can be used for transportation or as standalone storage solutions. They are perfect for distributors requiring flexibility in moving goods between locations or needing additional storage capacity during peak seasons.
- Advantages: Portability, suitable for transportation and storage, and available in various sizes.
- Considerations: Requires access to power for operation and may need specialized equipment for loading and unloading.
Blast Freezers
Blast freezers are designed for quick freezing of food products to preserve freshness and quality. They are essential for distributors dealing with products that must be frozen rapidly, such as seafood, meat, and prepared meals.
- Advantages: Rapid freezing reduces ice crystal formation, preserving the quality and texture of products.
- Considerations: High energy consumption and typically more expensive than conventional freezing methods.
Cold Storage Warehouses
Cold storage warehouses are large facilities used for storing vast quantities of perishable goods at controlled temperatures. They are essential for distributors needing significant storage capacity and are often equipped with advanced technology for inventory management and monitoring.
- Advantages: Large capacity, suitable for long-term storage, and can accommodate a wide range of products.
- Considerations: Requires significant investment and operational costs, including energy, labor, and maintenance.
Pharmaceutical Grade Cold Storage
Specifically designed to meet the stringent requirements of the pharmaceutical industry, these cold storage solutions maintain precise temperature and humidity levels essential for storing medications, vaccines, and other healthcare products.
- Advantages: High precision and reliability, equipped with advanced monitoring and alarm systems.
- Considerations: High cost of setup and operation, and strict regulatory compliance requirements.
Automated Cold Storage Facilities
Leveraging automation and robotics, these facilities optimize storage density, reduce labor costs, and improve operational efficiency. Automated cold storage is becoming increasingly popular for its ability to handle large volumes of products with minimal human intervention.
- Advantages: Increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced accuracy in inventory management.
- Considerations: High initial investment, complexity of system integration, and maintenance requirements.
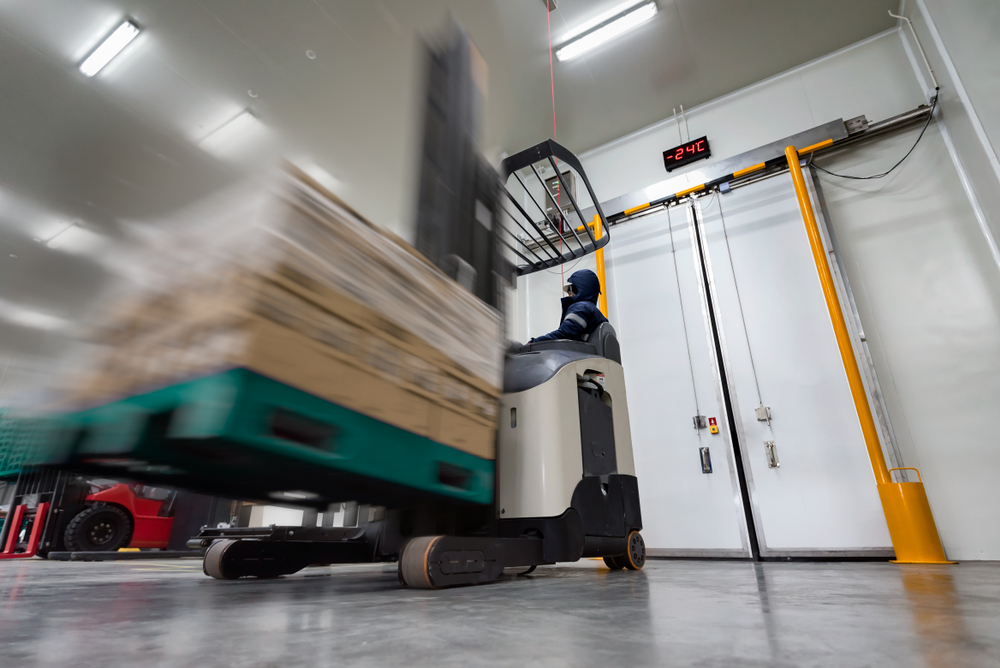

How Cooling is Achieved in Cold Storage Systems
The effectiveness of cold storage solutions hinges on their ability to maintain precise temperature control to preserve the integrity of perishable goods. This section delves into the key components of cold storage cooling systems and how they work together to achieve this goal:
Compressor
The heart of the refrigeration system, the compressor, plays a crucial role in the cooling process. It compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature, and moves it into the condenser. The type and size of the compressor vary based on the cold storage solution’s specific needs, influencing its efficiency and capacity.
Condenser
The condenser cools the heated refrigerant vapor from the compressor, converting it back into a liquid form. This component can be air-cooled, water-cooled, or evaporatively cooled, depending on the system’s design. The choice of condenser impacts the system’s overall energy efficiency and operational costs.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is a critical component that regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator. By controlling the amount of refrigerant, the expansion valve plays a key role in managing the cooling process’s efficiency and ensuring the desired temperature is maintained within the cold storage space.
Evaporator
Located inside the cold storage space, the evaporator absorbs heat from the environment, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the surrounding area. This process effectively removes unwanted heat from the storage area, maintaining the optimal temperature for preserving perishable goods.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the substance that circulates within the refrigeration system, undergoing phase changes from liquid to gas and back, facilitating heat exchange. The choice of refrigerant affects the system’s efficiency, environmental impact, and compliance with regulations.
Insulation
While not a direct part of the cooling system, insulation plays a vital role in maintaining cold storage efficiency. Proper insulation minimizes heat exchange between the cold storage interior and the external environment, reducing the cooling system’s workload and energy consumption.
Control Systems
Modern cold storage solutions are equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and adjust the cooling process. These systems ensure that temperatures are kept within precise limits, optimizing energy use and preventing temperature fluctuations that could compromise product quality.
Challenges in Cold Storage Management
Managing a cold storage facility efficiently involves navigating a variety of challenges that can impact both operational efficiency and profitability. Here are the top challenges faced by distributors:
- High Energy Costs: Cold storage facilities are energy-intensive, with refrigeration units running continuously to maintain precise temperatures. This results in high energy costs, which can significantly impact the bottom line.
- Specialized Equipment Needs: Cold storage requires specialized equipment such as refrigeration units, insulated panels, and temperature monitoring systems. Procuring and maintaining this equipment is costly and requires technical expertise.
- Strict Regulatory Compliance: Distributors must adhere to strict food safety and handling regulations, which vary by country and product type. Ensuring compliance requires constant vigilance and can incur additional costs for monitoring and documentation.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Maintaining consistent temperatures is crucial for product integrity. Temperature fluctuations can result from equipment failure, improper door sealing, or inefficient warehouse practices, leading to product spoilage.
- Supply Chain Complexity: The cold chain logistics involve multiple stages, including storage, transportation, and handling. Each stage presents potential risks for temperature deviations, making the entire supply chain complex to manage.
- Labor and Training Requirements: Skilled labor is essential for operating cold storage facilities effectively. Training staff on proper handling and storage procedures is crucial but can be challenging and resource-intensive.
- Sustainability Concerns: With increasing awareness of environmental issues, there is pressure to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and using eco-friendly refrigerants, which can require significant investment and innovation.
- Technological Integration: Implementing advanced technologies like IoT for temperature monitoring or automated systems for inventory management can be complex and expensive, yet they are increasingly necessary for competitive operations.
- Market Demand Fluctuations: Seasonal and market demand fluctuations can lead to periods of underutilization or overcapacity, challenging distributors to balance inventory levels and operational costs effectively.
- Infrastructure Limitations: In some regions, the lack of infrastructure, such as reliable power supply or suitable warehouse spaces, can limit the ability to establish or expand cold storage facilities.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, combining investment in technology, process optimization, and skilled workforce development. By acknowledging and tackling these issues head-on, distributors can enhance their cold storage management, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and profitability in their operations.

Tips for Optimizing Cold Storage Operations
Efficient management of cold storage facilities is crucial for distributors looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Here are key strategies for optimizing cold storage operations:
Conduct Regular Energy Audits
Identify areas where energy consumption can be reduced without compromising the quality of stored goods. This might include upgrading to more energy-efficient refrigeration systems, improving insulation, or installing energy management systems to monitor and control energy use more effectively.
Implement Inventory Management Best Practices
Adopting a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) approach ensures that older stock is used before newer stock, reducing the risk of spoilage. Additionally, using warehouse management systems (WMS) can help optimize storage space and streamline picking and packing processes.
Focus on Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance of refrigeration units, doors, and insulation systems can prevent unexpected breakdowns that lead to temperature fluctuations and product spoilage. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule is essential for the longevity of cold storage equipment.
Train Staff on Cold Storage Best Practices
Ensuring that all employees understand the importance of maintaining proper temperatures and the correct handling of perishable goods can significantly reduce the risk of product loss. Regular training sessions can keep staff updated on the latest cold storage protocols and technologies.
Explore Alternative Energy Sources
Investigating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can help reduce reliance on traditional energy sources and lower energy costs. Additionally, technologies like thermal energy storage systems can leverage off-peak energy rates to cool refrigerants, which then provide cooling during peak hours.
Leveraging Technology in Cold Storage
Advancements in technology offer new opportunities for distributors to enhance the efficiency and reliability of their cold storage operations. Here are some of the most impactful technological innovations:
IoT Sensors and Real-Time Monitoring
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors can monitor temperature and humidity levels in real-time, providing instant alerts if conditions deviate from set parameters. This allows for immediate action to prevent spoilage and ensures continuous compliance with regulatory standards.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS can significantly improve the efficiency of cold storage warehouses by automating the movement of goods. This reduces the need for manual handling, minimizes the time products spend outside of optimal temperature conditions, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Energy Management Systems (EMS)
EMS can optimize energy use throughout the facility, automatically adjusting temperatures based on real-time demand and external weather conditions. This not only reduces energy consumption but also ensures that products are stored in ideal conditions.
Advanced Insulation Materials
Innovations in insulation materials can significantly improve the thermal efficiency of cold storage facilities. Vacuum Insulated Panels (VIPs) and Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are examples of technologies that offer superior insulation properties, reducing energy consumption.
By implementing these strategies and embracing technological advancements, distributors can overcome many of the challenges associated with cold storage management. Optimizing operations not only leads to cost savings but also enhances product quality, safety, and sustainability, ultimately contributing to a more successful and resilient distribution business.
Related: 3 Key Reasons You May Need New Distribution Software

Ensuring Compliance and Safety in Cold Storage Operations
Maintaining compliance with food safety and handling regulations is paramount for distributors. Regulatory frameworks such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the United States, the European Union’s General Food Law, and other local regulations dictate strict standards for the storage and transportation of perishable goods. Here’s how distributors can ensure compliance and enhance safety:
Stay Informed on Regulations
Regularly update your knowledge of industry regulations and standards. This may involve subscribing to regulatory updates, attending industry conferences, and participating in training sessions. Staying informed helps you anticipate changes and adjust your operations accordingly.
Implement Comprehensive Tracking Systems
Utilize advanced tracking and documentation systems to maintain detailed records of storage temperatures, handling procedures, and product movements. This not only aids in regulatory compliance but also enhances traceability, allowing for quick response in case of a recall.
Conduct Regular Audits and Inspections
Schedule routine audits and inspections of your cold storage facilities to ensure they meet regulatory standards. This includes checking the functionality of temperature control systems, the integrity of insulation and seals, and the cleanliness of the storage environment.
Foster a Culture of Safety
Create a workplace culture that prioritizes safety and compliance. Encourage employees to report potential safety issues and provide regular training on the latest food safety practices and regulatory requirements. A well-informed and proactive team is your best defense against compliance breaches.
Implementing Efficient Cooling Solutions: Coolers and Freezers
As we already mentioned, many distribution operations, especially those serving convenience stores and smaller retail outlets, may not require large-scale cold storage warehousing. With this in mind, let’s focus on optimizing the coolers and freezers that form the backbone of these simpler cold storage capabilities. Here’s how to ensure these cooling solutions effectively meet your needs:
Optimizing Cooler and Freezer Use
- Strategic Placement: Position coolers and freezers to minimize the time products are out of optimal temperature conditions during receiving and shipping processes.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure coolers and freezers are regularly serviced to maintain efficiency, prevent breakdowns, and extend their lifespan.
- Temperature Monitoring: Implement simple, cost-effective temperature monitoring solutions to ensure products are stored at correct temperatures, safeguarding product quality.
DAC: The Optimal Solution for Convenience Store Distributors
For convenience store distributors, managing the distribution of refrigerated and frozen items efficiently is crucial. DAC, by CDR Software, is designed to optimize these operations, providing comprehensive inventory management, order processing, and distribution planning capabilities. DAC streamlines the distribution process, ensuring that perishable goods are handled efficiently and reach their destinations in optimal condition.
DAC’s features support operations that utilize coolers and freezers by:
- Enhancing Inventory Visibility: Offering real-time inventory tracking and management, ensuring that stock levels are maintained accurately, and products are replenished promptly.
- Improving Order Accuracy: Facilitating accurate order picking and packing, reducing errors, and ensuring that customers receive their orders correctly and on time.
- Efficient Warehouse Management: Streamlining warehouse operations with tools for better space utilization and workflow management, ensuring that perishable goods are stored and managed effectively within coolers and freezers.
Conclusion
For many distributors, particularly those serving the convenience store sector, the decision between implementing full-on cold storage warehousing and utilizing coolers and freezers comes down to understanding their specific operational needs and constraints.
For convenience store distributors in particular, DAC, by CDR Software, provides an intuitive solution tailored to streamline inventory management, enhance order accuracy, and improve overall operational efficiency. With DAC, managing your warehouse becomes straightforward, ensuring products are always stored in optimal conditions.
Learn more about how DAC can transform your distribution operations. Contact us today to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is cold storage important for convenience store distributors?
Cold storage is essential for storing perishable items like ice cream, dairy, beverages, and seasonal inventory. Proper temperature control preserves product quality, reduces waste, ensures safety, and supports retailer expectations for freshness and reliability.
What are the main challenges of managing cold storage in distribution?
Distributors often deal with high energy costs, temperature monitoring complexity, space optimization, spoilage risk, and coordination between warehouse handling and delivery routes. Maintaining consistent cold-chain integrity during transport is critical.
How can specialized software and technology support cold storage operations?
Purpose-built systems can automate temperature tracking, schedule regular maintenance, generate compliance reports, and integrate warehouse and delivery logistics. Alerts for temperature deviations and data logs help monitor performance and mitigate risk.
What best practices should distributors follow for effective cold storage management?
Keep precise temperature zones, perform regular equipment inspections, use real-time monitoring sensors, train staff on cold-chain protocols, implement first-in‑first‑out (FIFO) for perishable items, and maintain accurate inventory logs.
How does proper cold storage management benefit overall distributor performance?
Effective cold storage practices minimize spoilage and loss, improve inventory accuracy, enhance retailer trust, and support regulatory compliance—all of which lead to cost savings and consistently higher service levels.